From the heavy stone weights of ancient Egypt to the fitness trackers we wear on our wrists today, the concept of fitness has undergone profound changes. Formed over centuries, fitness as a cultural phenomenon has undergone many transformations, each reflecting the zeitgeist, the impact of technology and changing ideas about health and fitness. From ancient arenas to digital sports studios, this article takes you on a fascinating journey through the history of fitness to understand how ancient traditions and the latest scientific advances have influenced popular fitness trends and our attitudes toward physical activity.
Antiquity and Antiquity: The Foundation of Strength and Agility
Greece and the Olympic Games
For the ancient Greeks, physical fitness was not just a leisure activity, but a critical part of life related to military training and physical excellence. Introduced in 776 BC, the Olympic Games were the culmination of the Greek cultural and athletic world, reflecting a public respect for physical power and skill. These games included not only basic sports like running and discus throwing, but also more complex sports like wrestling and pentathlon, which required the ability to combine different physical skills in a single competition. This diversity of disciplines promoted comprehensive physical fitness, encouraging the development of various forms of exercise aimed at strengthening and harmonizing the body.
Rome and gladiatorial combat
In the Roman Empire, fitness culture was given a new expression through gladiatorial combat, considered a major entertainment and sporting event. Gladiators, being both professional athletes and spectacular performers, underwent intensive training that included not only traditional strength exercises, but also the study of various martial arts and the wielding of a variety of weapons. These trainings were conducted in special gladiator schools, where each student developed not only physical strength, but also tactical thinking, reaction and decision-making skills under extreme conditions. These aspects make the ancient Roman gladiator training system an early example of functional training, the aim of which was not only to improve physical qualities, but also to prepare for real combat.
The Middle Ages: Knights’ tournaments and hand-to-hand combat
In the Middle Ages, fitness for knights was closely intertwined with their military training, where the focus was on muscle strengthening and the ability to handle heavy weapons and armor. As part of the training process, knights’ tournaments were serious tests of agility, strength, and weapon proficiency. Various disciplines, such as jousting on lances, fencing and wrestling, not only demonstrated military skills but also helped to develop endurance and tactical thinking in knights.
Training was multi-faceted and included weight lifting, endurance and agility exercises, and the mental aspects of military strategies. This not only prepared knights physically but also mentally for real battles, making them some of the most physically fit and tactically competent warriors of their time.
The eighteenth and nineteenth centuries: The birth of modern sport

Gymnastics in Germany
At the dawn of the 19th century, Friedrich Ludwig Jahn, a German educator, played a key role in shaping modern gymnastics by developing a system of exercise that has had a significant impact on physical education in Europe and beyond. The system he created in 1811, known as “Turnkunst” (from the German “Turnen” – to exercise and “Kunst” – art), included exercises on the rings, bars and crossbar, as well as complex exercises on the ground that focused on developing strength, flexibility and coordination. Jan sought not only to strengthen the body, but also to nurture the spirit through physical education, which has become the basis for many of today’s educational and sports programs.
The development of running in Britain
At the same time in Britain, the 18th century brought with it a revival of interest in long-distance running. This time was an important period for the development of running as a sporting discipline, when organized competitions began to be held and modern athletics was born. Running, originally practiced mainly in rural areas as part of festivals and fairs, was transformed into a structured sport with rules and standards for competition. This not only helped to popularize physical culture among the general public, but also marked the beginning of sports science, which began to investigate optimal training and recovery methods for athletes.
The 20th Century: The Age of Innovation and Mass
In 1968, Dr. Kenneth Cooper published the book Aerobics, which had a revolutionary impact on the global health and fitness community. This book not only popularized aerobic exercise, but also introduced the scientific basis for its use in improving cardiovascular and overall health. Aerobics became especially popular in the 1980s, when a boom in healthy lifestyles began in Western culture. Key points in the popularization of aerobics include:
- The development of aerobic programs in sports clubs.
- The creation of specialized aerobic videos that made workouts accessible at home.
- The introduction of music to make workouts more entertaining and rhythmic.
Development of bodybuilding
Bodybuilding took a new turn in the 1970s thanks to the influence of celebrities such as Arnold Schwarzenegger, whose achievements and media image played a key role in popularizing the sport. The influence of Schwarzenegger and his contemporaries led to a significant increase in interest in strength training and bodybuilding as a way to achieve perfect fitness. The main aspects of bodybuilding’s growing popularity included:
- The distribution of bodybuilding magazines and books that offered training methods and diets.
- The organization of competitions, such as Mr. Olympia, which attracted public and media attention.
- Developing sports nutrition, including the introduction of protein supplements and other products to support intense training and recovery.
The twenty-first century: The digital age and globalization
Yoga and meditation
At the beginning of the 21st century, the world has largely turned its attention to the importance of psychological well-being, which has led to a massive proliferation of yoga and meditation. These practices, rooted in ancient traditions, have become popular in many countries as a means of improving not only physical but also mental fitness. The main factors behind the popularization of yoga and meditation include:
- Psychological benefits: Scientific studies have confirmed that regular practice of yoga and meditation helps in reducing stress, improving concentration and overall emotional well-being.
- Accessibility: Yoga and meditation are easily adapted for practice at home or in specialized studios, making them accessible to a wide audience.
- Social media and networks: The popularity of these practices with celebrities and influencers on social media has greatly increased their visibility and appeal.
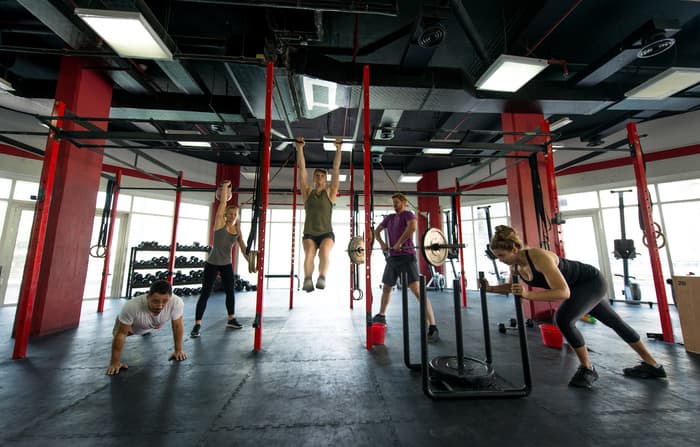
Functional training
Launched in 2000, Crossfit and other forms of functional training have quickly gained popularity by emphasizing all-round physical development. These workout programs focus on mimicking natural human movement and include exercises that develop strength, flexibility, speed, and endurance. Benefits of functional training include:
- Increased functional strength: Exercises are packed with movements that improve daily activity and enhance overall performance.
- Community: The community culture around programs like Crossfit creates a motivating and supportive atmosphere.
Technology in fitness
With the advancement of smart technology and the internet, the possibilities for personalized and affordable workouts have greatly expanded. Smartwatches, fitness bracelets and mobile apps allow users to track their physical metrics such as heart rate, step count, sleep quality and calories consumed, encouraging a more informed approach to exercise. Key points on incorporating technology into fitness:
- Personalization: Technology enables the creation of customized workout plans based on the user’s personal data and goals.
Motivation and analytics: Apps and devices provide feedback and analytics that motivate users to work out regularly and track progress.